Research progress on synergistic extraction of typical organophosphorus extractant in solvent extraction
Hao ZHANG, Guohua YE, Ziyang CHEN, Yu XIE, Qi ZUO
The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering
2021, 21 ( 7):
741-751.
DOI: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220179
As a branch of solvent extraction, synergistic extraction has been widely studied. In order to explore the mechanism of synergistic extraction, it is necessary to clarify the internal reasons of the extraction system and give the relationship between the micro and macro properties. Therefore, it is important to understand the synergistic extraction system and the influencing factors from the microscopic structure and internal movement of molecules. In this owrk, the mechanism of synergistic action between extractant, extractant and metal ions and the influencing factors were reviewed. It pointed out that the essence of synergistic extraction was the formation of hydrogen bonds, which led to the change of the structure and energy of extractant, thus improving the extraction effect. Synergistic extraction mainly includes two aspects: one is easier to generate stable extraction complex to improve the extraction efficiency; the other is to improve the separation performance by using the difference between extractant. The pH of the extraction system, the combination and proportion of different extractant, the concentration of extractant and the addition of neutral phosphorus extractant significantly affect the synergistic extraction process, and there are interactions among various factors. It will be one of the effective methods in the field of chemical research in the future to carry out theoretical prediction by simulation calculation, verify by experimental means, and characterize with modern analytical chemistry method. The theory is popularized to practice, so as to better guide the production.
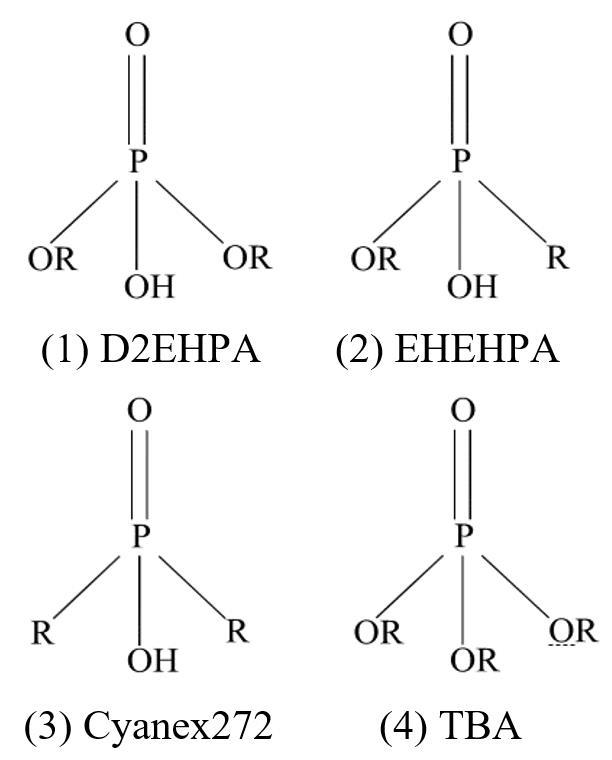
Fig.1
Structure diagram of typical organic phosphorus extractants
Extracts from the Article
有机磷类萃取剂是众多萃取剂中常用的一种,在溶剂萃取中主要用于萃取稀土金属及碱土金属[10-13],常见的磷类萃取剂主要包括酸性、中性磷类及醇类萃取剂。酸性磷类萃取剂主要包括常用的D2EHPA (P204)[14-17],EHEHPA (PC88A或P507),氰胺公司推出的Cyanex系列,如Cyanex272 (2,4,4-三甲基戊基)磷酸、Cyanex923、Cyanex921 (直链三烷基氧化膦)、Cyanex301 [双(2,4,4-三甲基戊基)二硫代磷酸酯]及比较新型的Cyphos IL 101 [三己基(十四烷基)溴化膦]、Cyphos IL 102 (溴化十六烷基膦)等[18-23]。酸性萃取剂主要结构为中心磷原子上连着一个羟基与酰基,金属离子通过离子交换与磷羟基的氢进行交换从而与萃取剂结合[20]。磷酰基有很强的电负性,并且有一对孤对电子,可以与部分金属离子形成配位化合物,甚至生成螯合物[24]。中性磷类萃取剂主要为TBP, DBBP, TBPO等,中性磷类萃取剂结构中不含磷羟基,有三个氧酯基,因此磷酰基上的电荷密度更加集中,在萃取过程中的表现形式更多样,不仅可以作为萃取剂还可以作为改性剂。本工作主要介绍四种典型常见的有机磷类萃取剂,包括D2EHPA (P204), EHEHPA (PC88A或P507), Cyanex272, TBP,其结构见图1,四种萃取剂的中心磷原子均以不等性的sp3杂化[25],呈四面体结构。分子中负电荷主要集中在磷酰基和羟基的氧原子上,正电荷主要集中在中心磷原子上,磷酰基和羟基是萃取剂分子反应活性的中心。被萃取物会与磷羟基上的氢原子发生离子交换或磷酰基的氧发生络合反应而吸附于萃取剂分子上,因此两种基团中心原子的电荷分布及能量的细微变化都会引起萃取剂性质的极大改变。随着与中心磷原子相连的氧原子数目的增多和给电子烷基数目的减少,中心磷原子电荷密度分布大小为D2EHPA>EHEHPA>Cyanex272,中心磷原子的正电荷会影响磷酰基与磷羟基上的负电荷密度。磷酰基与磷羟基中氧原子电荷密度大小均为D2EHPA>EHEHPA>Cyanex272,磷酰基上电荷密度增加会加强其与金属离子的配位能力。磷羟基上电荷密度的增加会加强其与质子的结合能力,从而减弱对金属离子的萃取能力。磷羟基上的氧与氢原子的电荷密度差随吸电子基团数目的减少而减少,导致氢离子解离常数降低,萃取性能变差。四种萃取剂中D2EHPA氧酯基数量最多,氧原子电荷最集中,氧原子与氢原子电荷密度差最大,因此萃取性能最强,但选择性较差,Cyanex272则与之相反。Cyanex272电荷密度较D2EHPA低,磷羟基上的氢更容易解离,因此酸度较高,可以在较高pH下萃取且更容易反萃。四种典型磷类萃取剂主要区别在与磷相邻的基团上,因为四种萃取剂所连基团不同,导致其性质不同,包括萃取性能、分离性能、反萃取性能等,其中1~3号为酸性萃取剂,4号为中性萃取剂。其萃取能力大小顺序为D2EHPA>EHEHPA>Cyanex272>TBP[25]。
将不同类型的萃取剂按一定浓度、比例、pH混合,在萃取部分金属时,可产生较单一萃取剂更好的萃取效果,这种效果包括萃取率、分离性能、反萃性能等,并且被多次试验所证实。很多文献提出了协同萃取中共萃物的形成,但并未深入阐明协同萃取效果强于单一萃取的原因,为充分利用协萃效应,必须更深入地探索协同萃取分子层面的机理。如图1所示,1~3三种酸性有机磷类萃取剂结构,均含一个磷酰基与一个羟基,导致不同萃取剂之间的羟基会发生氢键缔合效应从而形成二聚体[31,32],氢键的产生会直接影响萃取剂分子的结构,使萃取剂本身性质发生细微改变,从而影响萃取效果。还会影响萃取剂与金属结合生成萃和物的反应过程,在一定条件下可以加速萃合物的生成,并且使其更稳定[32]。魏昶[25]通过量子化学泛密度函数理论中的B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p)方法对三种萃取剂进行结构分析。从结构上来看,氢键的形成导致单体分子中电荷发生了转移,使二聚体分子中所有键长均变长,尤其是磷酰基(P=O)与磷羟基(P-O-H),见表1。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|